which imbalance results when systemic arterial blood co2 levels raise to abnormal values?
 Solved: 12. This Is The Largest Single Component Of The Hu... | Chegg.com
Solved: 12. This Is The Largest Single Component Of The Hu... | Chegg.comCh. 27- Fluids, electrolytes, acid/base...33cards How much of the total volume of body fluid is intracellular fluid? A) 10% B) 50% C) 1/3 D) 2/3 E) 99%This imbalance results when systemic arterial CO2 levels increase to abnormal values. A) Metabolic alkalosis B) metabolic acidosis C) respiratory acidosis D) Respiratory alkalosis E) None of these optionsCOMPANYLEGAL " POLICIESCHEG PRODUCTS AND SERVICESCHEGG NETWORKCUSTOMER SERVICE© 2003-2021 Chegg Inc. All rights reserved.

SC131 Unit 7 Quiz.docx - Inadequate exhalation of carbon dioxide can cause Blood pH to drop Alkalosis Respiratory compensation Unequal distribution of | Course Hero

Which imbalance results when systemic arterial blood CO 2 levels raise to | Course Hero

Which imbalance results when systemic arterial blood CO 2 levels raise to | Course Hero

In partial compensation a pH is brought into the normal range b systemic | Course Hero

SC131 Unit 7 Quiz.docx - Inadequate exhalation of carbon dioxide can cause Blood pH to drop Alkalosis Respiratory compensation Unequal distribution of | Course Hero

SC131 Unit 7 Quiz.docx - Inadequate exhalation of carbon dioxide can cause Blood pH to drop Alkalosis Respiratory compensation Unequal distribution of | Course Hero

In partial compensation a pH is brought into the normal range b systemic | Course Hero

In partial compensation a pH is brought into the normal range b systemic | Course Hero
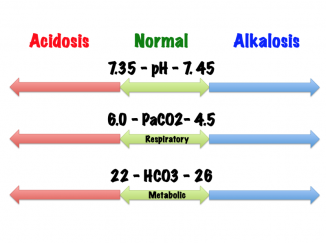
Arterial Blood Gases - Physiopedia

How much of the total volume of body fluid is intracellular Which | Course Hero

How much of the total volume of body fluid is intracellular Which | Course Hero
Cureus | Bicarbonate Therapy for Critically Ill Patients with Metabolic Acidosis: A Systematic Review

Inadequate exhalation of carbon dioxide can cause a Blood pH to drop b | Course Hero

Arterial Blood Gases - Physiopedia

SC131 Unit 7 Quiz.docx - Inadequate exhalation of carbon dioxide can cause Blood pH to drop Alkalosis Respiratory compensation Unequal distribution of | Course Hero

Which of the following is a condition where blood pH is below 735 a Isodosis b | Course Hero
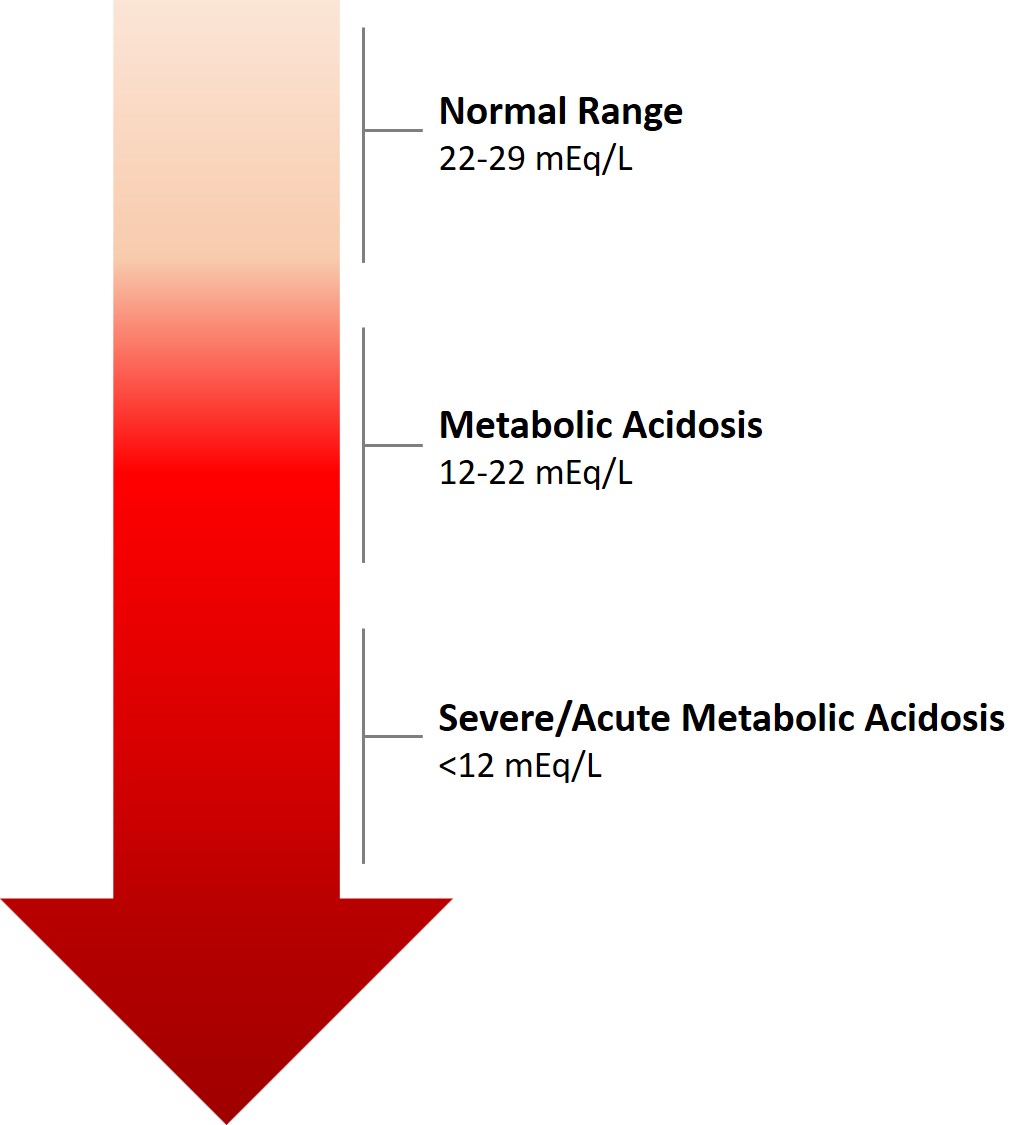
Metabolic acidosis - Wikipedia

Arterial Blood Gases - Physiopedia
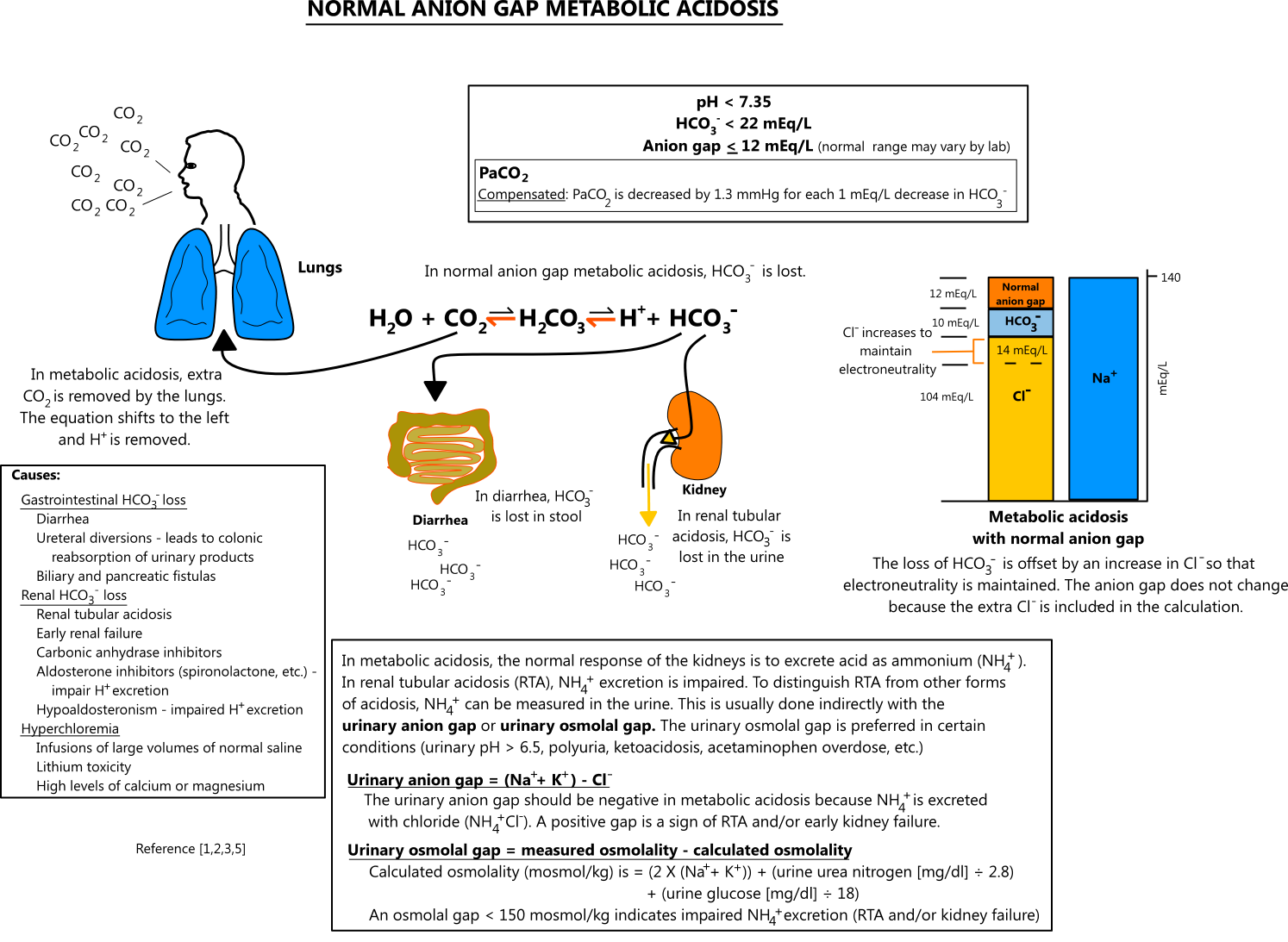
Acid-base disorders

The arterial blood gas algorithm: Proposal of a systematic approach to analysis of acid-base disorders - ScienceDirect

Gas exchange and ventilation–perfusion relationships in the lung | European Respiratory Society

ABG Interpretation: The Ultimate Guide to Arterial Blood Gases

Arterial Blood Gas (ABGs) Analysis Ultimate Guide - Nurseslabs

Arterial Blood Gases and Oxygen Content in Climbers on Mount Everest | NEJM

Acid-Base Imbalance - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics
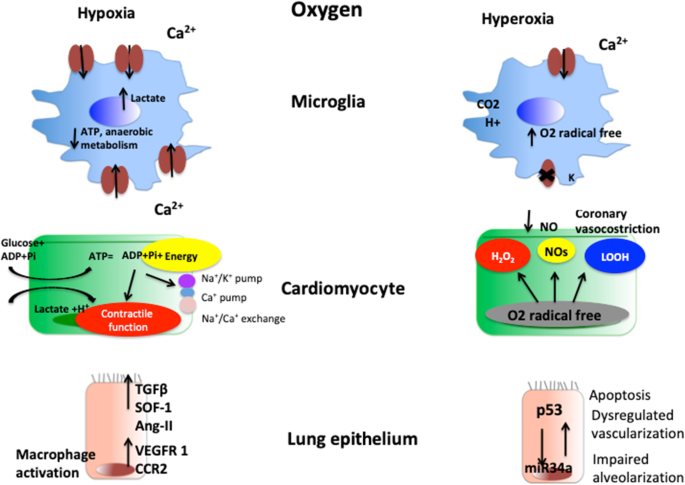
Pathophysiology and clinical consequences of arterial blood gases and pH after cardiac arrest | Intensive Care Medicine Experimental | Full Text

Easy blood gas analysis: Implications for nursing - ScienceDirect

SC131 Unit 7 Quiz.docx - Inadequate exhalation of carbon dioxide can cause Blood pH to drop Alkalosis Respiratory compensation Unequal distribution of | Course Hero

Cerebrospinal Fluid pH - an overview | ScienceDirect Topics

Chemical Control of Breathing

Retinal oximetry and systemic arterial oxygen levels - Eliasdottir - 2018 - Acta Ophthalmologica - Wiley Online Library

Umbilical cord arterial and venous gases, ionogram, and glucose level for predicting neonatal morbidity at term - European Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology and Reproductive Biology

Phylogenic Determinants of Cardiovascular Frailty, Focus on Hemodynamics and Arterial Smooth Muscle Cells | Physiological Reviews

Transport of Oxygen and Carbon Dioxide (Study Guide)

Retinal oximetry and systemic arterial oxygen levels - Eliasdottir - 2018 - Acta Ophthalmologica - Wiley Online Library

Easy blood gas analysis: Implications for nursing - ScienceDirect
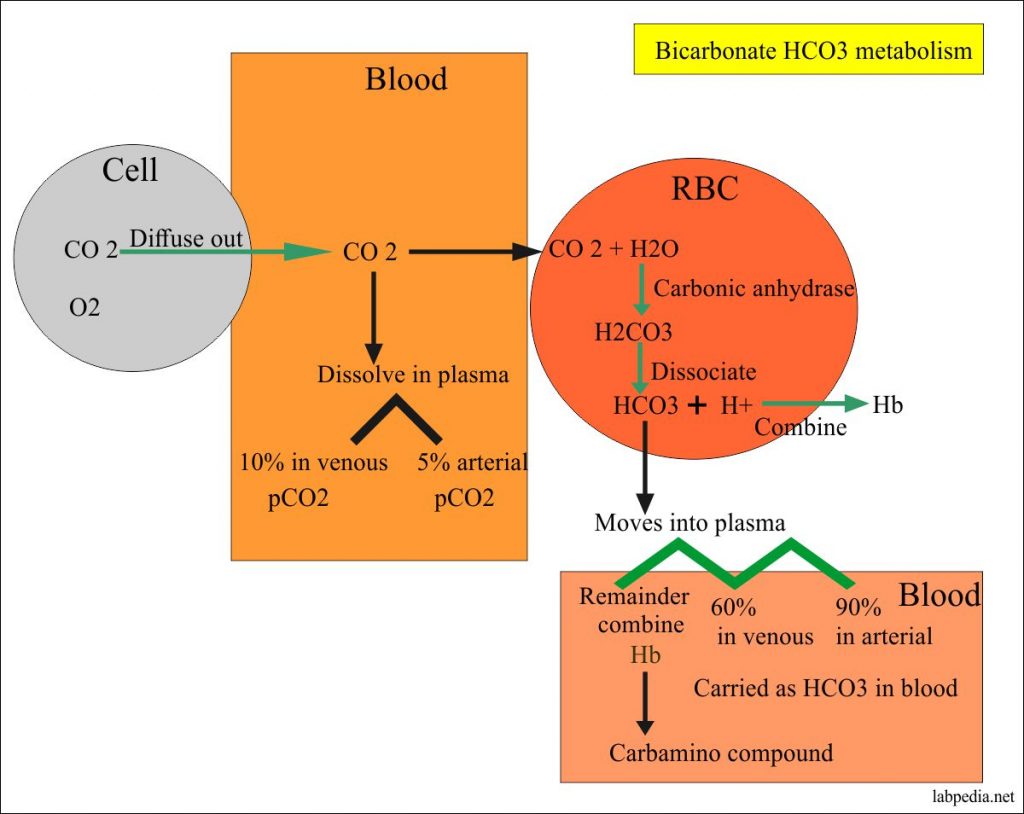
Acid-base Balance:- Part 4 – Bicarbonate Level (HCO3-) – Labpedia.net

Arterial Blood Gases - Physiopedia

Electrolyte and Acid–Base Disturbances in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus | NEJM
Posting Komentar untuk "which imbalance results when systemic arterial blood co2 levels raise to abnormal values?"